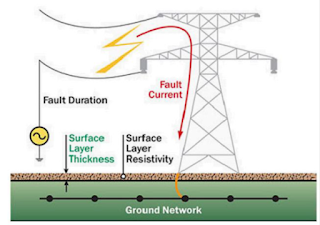
Lightning Arrester

Lightning Arrester surges in Power system cause damage to main station equipment and overhead lines, so they must be protected from the risk of lightning strikes. Apart from lightning, some switching operations and faults may also generate overvoltages that can be potentially hazardous to the insulation of the substation equipment and insulation of the lines, These devices have many names as surge suppressors, surge diverters, and lightning arresters . These devices are placed parallel to the device to be protected, The purpose of lightning arresters is to provide a path over which the surge can pass to the ground. When a lightning impulse or switching surge reaches the arrester terminals, it causes a spark which jumps across the air gaps, passes through the non-linear resistive element, Sic, which allows a low resistance for the high voltage surge, but presents a high resistance under the rated voltage of the lines. In other words, the lightning arrester leads off only the su...